Search Strategies
Simple Search
The simple search uses keywords only. Once “Go” is pressed, speechBITE will then search for the keyword/s in the title, author, source and abstract of all articles stored within the database (at that point in time).
Tip: Make sure your spelling is correct, the database does not match misspelled words.
When using the simple keyword search (to increase your success when searching the database), try to use:
- One or two keywords only (e.g. language therapy)
- Inverted commas to search for an exact phrase (e.g.
"language therapy")
In general, speechBITE assumes the word “AND” between each keyword in the simple search box. For example, a search for aphasia therapy will return articles that contain both terms aphasia AND therapy.
Advanced Search
Text boxes
The text boxes at the top of the advance search page can be used to include search terms within the following fields:
- Keyword (general)
- Author

Dropdown Menus
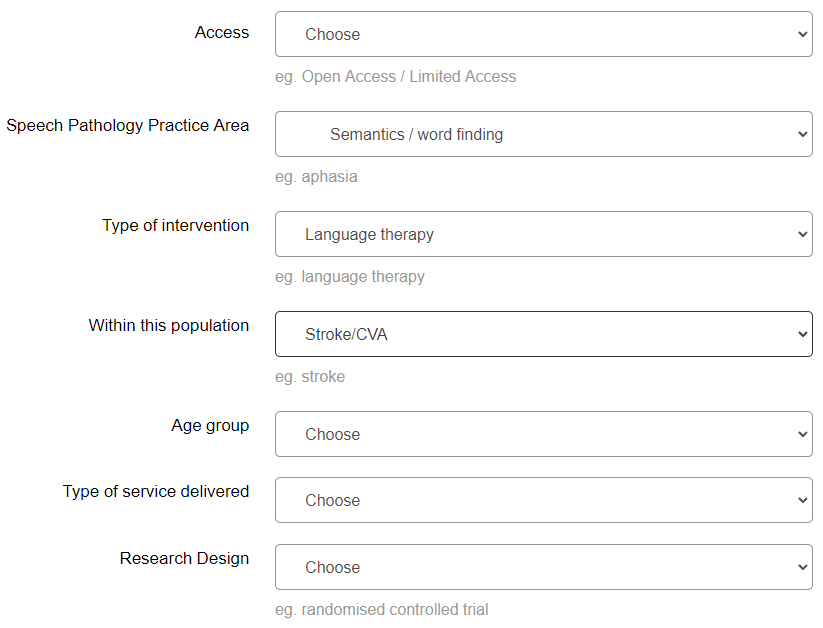
To further refine your search, use the drop-down menus. You can use the drop-down menus only or a combination of drop-down menus and a keyword search. For example, you could select to search for all articles targeting language therapy for word-finding difficulties (semantics) post stroke:
Searching for Ratings
If you want to further refine your search to include only articles that have been rated and received a rating above a certain number, you can do so by entering a number in the ‘PEDro-P rating of at least’ field. For example, if you wanted to only include group comparison papers (RCTs and Non-RCTs) that received a rating of 6 or above on the PEDro-P scale:

Tips for keyword searching
In general, an assumed “AND” is used for spaces between terms.
Thus, a search for dysphagia treatment in the keyword field will match any document that includes the terms both dysphagia AND treatment.
The following table provides a list of general search guidelines when using keywords when searching speechBITE.
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Boolean operators | Use AND to create a more complex search. | language AND therapy will yield search results that include both terms |
| Wildcard truncation | Use an asterisk (*) to search for multiple characters before, within, or after a search string. | *phasia will yield search results that include both aphasia and dysphasia |
| Exact phrase search | Insert a term within quotation marks to create an exact match. Note that no search method is case sensitive, thus "LANGUAGE" matches the same results as "language", or "Language". |
"language therapy" matches the phrase in exactly that word sequence |
| Spelling | Small spelling variants are NOT matched. The term randomised will not currently match randomized. For these known spelling variants, use an asterisk (*) to search for multiple characters before, within, or after a search string. | randomi*ed |
| Plurals | Pluralised forms of words will NOT currently match singular versions (and vice versa). The term drugs will find ONLY drugs. To match both the singular and plural form of terms, use an asterisk (*). | drug* |
| Diphthong characters | Terms with spelling variations that include diphthongs should be searched with a wildcard character to ensure that all forms of a term are matched. | isch*mic |
| Stop words | Words such as “in,” “the” and “of” are matched in the search. The Boolean search operator AND is the only term treated as a stop word. | |
| Accented characters | For all fields, accented characters are not matched by their equivalent unaccented form. To match accented characters use the following options: 1) Use the wildcard character (*) for a broad match, or 2) if the term is displayed on a page you are viewing, copy and paste it to the search box. | M*ori will yield search results that include both Māori and Maori |
Why does my search find no articles or very few articles?
Your search may return none or very few results for any of the following reasons:
- Incorrect spelling – the database will not match misspelled words.
- There may be no articles that meet the inclusion criteria for speechBITE in the areas that you are searching.
- A lack of published research in that area.
- Your search terms may be too narrow.
Try broadening your search terms or using a smaller number of search terms to see if this changes your results.
For example, if you were searching for treatment articles investigating the use of neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES/e-stim) for dysphagia post stroke, the following search terms get different results:
| Example | Search terms used | No. of results |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Keywords: e-stim Speech Pathology Practice Area: Dysphagia Type of intervention: Assistive devices/technological interventions Within this population: Stroke Age group: Adults Type of service delivered: Individual |
1 |
| 2 | Keywords: neuromuscular electrical stimulation Speech Pathology Practice Area: Dysphagia Type of intervention: Assistive devices/technological interventions Within this population: Stroke Age group: Adults Type of service delivered: Individual |
25 |
| 3 | Speech Pathology Practice Area: Dysphagia Type of intervention: Assistive devices/technological interventions Within this population: Stroke |
92 |
Why are there some papers that do not have ratings?
At present there are two types of group comparison designs with ratings on speechBITE: randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and non-randomised controlled trials (NRCTs). Systematic reviews, case series, single-case designs, and clinical practice guidelines are not rated for quality on speechBITE.
In order to reach a consensus rating on the paper, it is required that the treatment studies be reviewed by two independent raters. If there is a discrepancy between the two raters, a third rater provides a consensus decision on the discrepancy. This process takes time due to the nature of raters working as volunteers for speechBITE. Ratings are continually added once a consensus decision is reached. Currently speechBITE contains PEDro-P ratings for approximately 80% of the listed group comparison papers (RCTs and NRCTs).
How do I access the full text of journal papers listed on speechBITE?
speechBITE does not provide the full text of journal articles. However, whether an article is available as open access or behind a paywall is indicated in the record. Open access articles can be reached by clicking the link under “Access”. For articles that are behind a paywall, you can choose to print, email, save, or export the citation details and then either visit your local academic library and find the appropriate journal or access the on-line journal via your academic library website. Some professional associations and organisations provide access to on-line journals for members and staff. For example, members of Speech Pathology Australia have free online access to the International Journal of Speech-Language Pathology. Members of the American Speech-Language Hearing Association have on-line access to the Journal of Speech, Language and Hearing Research, American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, Language Speech and Hearing Services in Schools and the American Journal of Audiology. Copyright permission is also required to publish the abstracts on speechBITE. If an abstract is not available on speechBITE, then copyright permission has not been obtained.
Looking for answers for other frequently asked questions?
